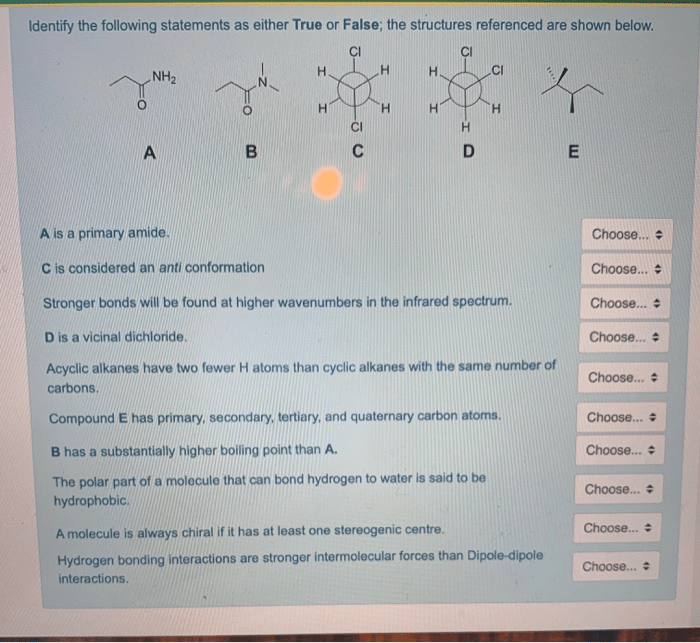
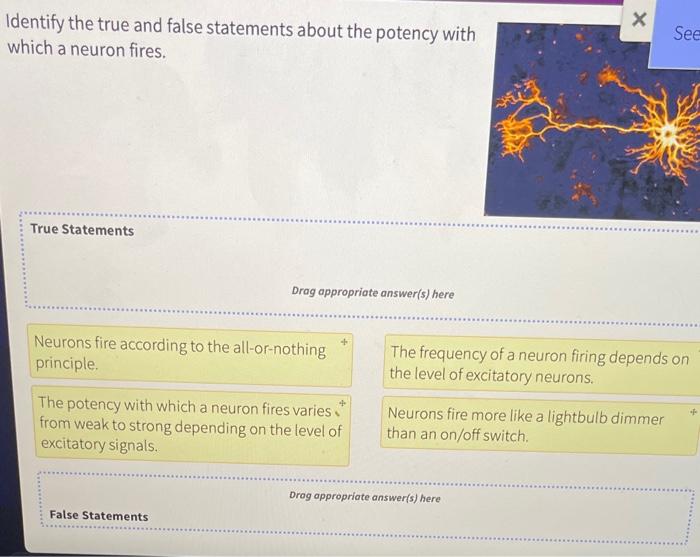
Identify the true and false statements about automatic mimicry. – Delving into the realm of automatic mimicry, we embark on a journey to separate fact from fiction. This phenomenon, characterized by involuntary imitation, presents intriguing questions that we shall unravel through careful examination and analysis.
To guide our exploration, we present a table categorizing statements about automatic mimicry as either true or false. This comparative approach allows us to establish a clear understanding of its mechanisms, benefits, and limitations.
Automatic Mimicry

Automatic mimicry is a form of mimicry in which one species (the mimic) evolves to resemble another species (the model) to gain an advantage, such as protection from predators or increased access to food.
Key characteristics of automatic mimicry include:
- The mimic and model species are often very different in appearance.
- The mimic’s resemblance to the model is often very specific and detailed.
- The mimic’s resemblance to the model is often adaptive, meaning that it provides the mimic with some sort of advantage.
Examples of automatic mimicry include:
- The viceroy butterfly, which mimics the monarch butterfly, a poisonous species that predators avoid.
- The cuckoo bird, which mimics the eggs of other bird species, allowing it to lay its own eggs in their nests.
- The orchid mantis, which mimics the appearance of an orchid flower to attract prey.
Questions Often Asked: Identify The True And False Statements About Automatic Mimicry.
What are the key characteristics of automatic mimicry?
Automatic mimicry involves involuntary imitation, often triggered by specific stimuli or situations. It differs from conscious or learned imitation, occurring without conscious effort or awareness.
How does automatic mimicry benefit the mimic?
Mimicry provides a survival advantage by enabling the mimic to resemble a more formidable or less desirable species, thereby reducing the risk of predation or increasing access to resources.
What are the limitations of automatic mimicry?
Automatic mimicry can be constrained by genetic variation, environmental factors, and the ability of predators or prey to distinguish between mimics and their models.