Khanates ap world history definition – Khanates, defined as nomadic or semi-nomadic polities ruled by a khan, have played a pivotal role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of Eurasia throughout history. This comprehensive exploration delves into the etymology, characteristics, historical examples, and lasting impact of khanates, providing an in-depth understanding of their significance in AP World History.
The term “khanate” originates from the Turkic word “khan,” meaning “ruler” or “leader.” Khanates typically exhibited a hierarchical political structure, with the khan holding absolute authority and supported by a council of advisors. These polities often existed in complex relationships with neighboring empires and kingdoms, sometimes as vassals or allies, and at other times as independent entities.
Definition of Khanates
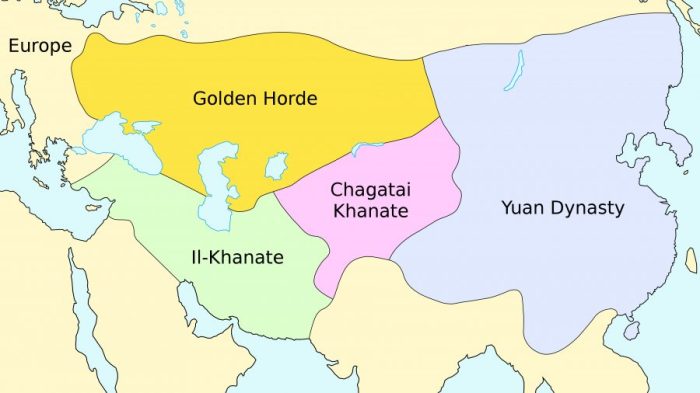
A khanate is a political entity ruled by a khan, a title of Mongol or Turkic origin meaning “ruler” or “leader.” Khanates emerged in Central Asia during the Mongol Empire and spread throughout Eurasia, leaving a lasting impact on the political and cultural landscape.
Khanates were typically characterized by a decentralized political structure, with the khan exercising absolute authority within their domain. The khan was supported by a hierarchy of nobles and military leaders, who held their positions based on merit and loyalty.
Khanates often maintained complex relationships with other political entities, such as empires and kingdoms. They could be vassals, allies, or even rivals, depending on the balance of power and the diplomatic skills of the khan.
Characteristics of Khanates
Khanates shared certain characteristics that distinguished them from other political entities:
- Decentralized Political Structure:Khanates were typically decentralized, with the khan exercising authority over a vast territory through a network of governors and military commanders.
- Absolute Authority of the Khan:The khan held absolute power within their domain, making all political and military decisions. They were often regarded as divine rulers or representatives of the gods.
- Merit-Based Hierarchy:Positions within the khanate were often based on merit and loyalty, rather than hereditary succession. This allowed for talented individuals to rise through the ranks.
- Complex Relationships with Other Entities:Khanates often maintained complex relationships with neighboring empires and kingdoms, ranging from alliances to vassalage.
Historical Examples of Khanates
Numerous khanates emerged throughout Eurasia, each with its own unique history and significance:
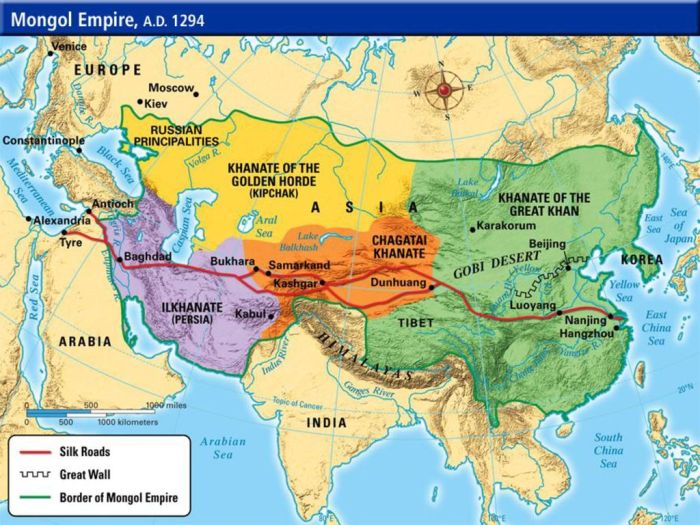
- Mongol Khanates:The Mongol Empire fragmented into several khanates after the death of Genghis Khan, including the Golden Horde, the Ilkhanate, and the Chagatai Khanate.
- Kazakh Khanate:Established in the 15th century, the Kazakh Khanate ruled over the vast steppes of Central Asia until the Russian conquest in the 19th century.
- Crimean Khanate:Located in the Crimean Peninsula, the Crimean Khanate was a vassal of the Ottoman Empire from the 15th to the 18th centuries.
- Khanate of Kazan:The Khanate of Kazan was a powerful Muslim state in the Volga region, conquered by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century.
Impact of Khanates on World History, Khanates ap world history definition
Khanates played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of Eurasia:
- Political Expansion and Empire Building:Khanates were often at the forefront of political expansion, establishing vast empires that stretched across vast territories.
- Spread of Ideas and Technologies:Khanates facilitated the spread of ideas, technologies, and religions across Eurasia, connecting different cultures and fostering cultural exchange.
- Cultural Legacy:Khanates left a lasting cultural legacy, including architectural monuments, literary works, and traditions that continue to influence societies today.
Question Bank: Khanates Ap World History Definition
What is the etymology of the term “khanate”?
The term “khanate” originates from the Turkic word “khan,” meaning “ruler” or “leader.”
What was the typical political structure of a khanate?
Khanates typically exhibited a hierarchical political structure, with the khan holding absolute authority and supported by a council of advisors.
What was the relationship between khanates and other political entities?
Khanates often existed in complex relationships with neighboring empires and kingdoms, sometimes as vassals or allies, and at other times as independent entities.