Compute the gross profit for fifo method and lifo method. – Delving into the realm of inventory valuation, this discourse explores the intricacies of computing gross profit using the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) and LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) methods. These techniques play a pivotal role in determining the cost of goods sold and, consequently, the profitability of an enterprise.
The FIFO method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, while the LIFO method assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first. Understanding the nuances of these methods is crucial for accurate financial reporting and informed decision-making.
Compute Gross Profit using FIFO Method
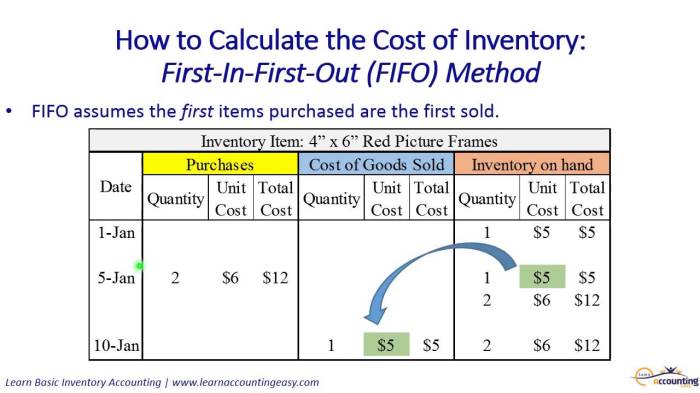
FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method assumes that the first units purchased are the first units sold. This method is often used when the cost of goods sold is relatively stable or increasing over time.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Calculating Gross Profit using FIFO
- Determine the beginning inventory.
- Add the cost of goods purchased during the period.
- Subtract the ending inventory (using the cost of the first units purchased).
- The resulting amount is the cost of goods sold.
- Subtract the cost of goods sold from the net sales to obtain the gross profit.
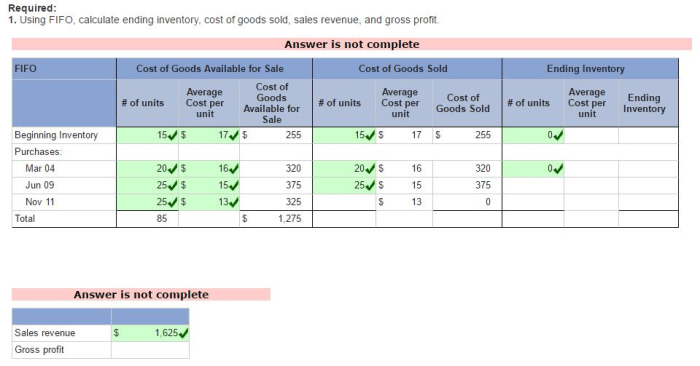
Example of FIFO Method
- Beginning inventory: 100 units at $10 per unit = $1,000
- Goods purchased: 200 units at $12 per unit = $2,400
- Ending inventory: 50 units at $12 per unit = $600
Cost of goods sold = $1,000 (beginning inventory) + $2,400 (goods purchased) – $600 (ending inventory) = $2,800
Gross profit = $5,000 (net sales) – $2,800 (cost of goods sold) = $2,200
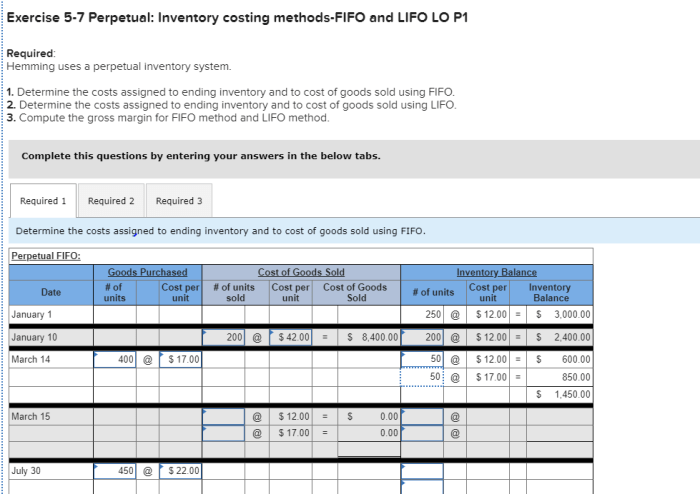
Compute Gross Profit using LIFO Method
LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) method assumes that the last units purchased are the first units sold. This method is often used when the cost of goods sold is relatively volatile or decreasing over time.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Calculating Gross Profit using LIFO
- Determine the ending inventory.
- Subtract the cost of goods purchased during the period.
- Add the beginning inventory (using the cost of the last units purchased).
- The resulting amount is the cost of goods sold.
- Subtract the cost of goods sold from the net sales to obtain the gross profit.
Example of LIFO Method
- Beginning inventory: 100 units at $10 per unit = $1,000
- Goods purchased: 200 units at $12 per unit = $2,400
- Ending inventory: 50 units at $12 per unit = $600
Cost of goods sold = $600 (ending inventory) – $2,400 (goods purchased) + $1,000 (beginning inventory) = $1,000
Gross profit = $5,000 (net sales) – $1,000 (cost of goods sold) = $4,000
Comparison of FIFO and LIFO Methods
FIFO and LIFO methods can result in different gross profit amounts. The following table compares the key features of these two methods:
| Feature | FIFO | LIFO |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Valuation | First units purchased | Last units purchased |
| Gross Profit | Lower in inflationary periods, higher in deflationary periods | Higher in inflationary periods, lower in deflationary periods |
| Tax Implications | Lower taxable income in inflationary periods | Higher taxable income in inflationary periods |
Advantages and Disadvantages of FIFO and LIFO Methods
Advantages of FIFO Method
- Provides a more accurate measure of current cost of goods sold.
- Simpler to implement and manage.
- Matches the physical flow of goods.
Disadvantages of FIFO Method, Compute the gross profit for fifo method and lifo method.
- Can result in lower gross profit during inflationary periods.
- May not reflect the actual cost of goods sold, especially during periods of rapidly changing prices.
Advantages of LIFO Method
- Can result in higher gross profit during inflationary periods.
- Provides a more conservative measure of inventory valuation.
- Can reduce taxable income during inflationary periods.
Disadvantages of LIFO Method
- Can result in lower gross profit during deflationary periods.
- May not reflect the actual cost of goods sold, especially during periods of rapidly changing prices.
- More complex to implement and manage.
Considerations for Choosing FIFO or LIFO Method
The choice between FIFO and LIFO methods depends on several factors, including:
- The nature of the business
- The rate of inflation
- The company’s tax strategy
In general, FIFO is more appropriate for businesses with stable or increasing costs of goods sold, while LIFO is more appropriate for businesses with volatile or decreasing costs of goods sold.
FAQ Explained: Compute The Gross Profit For Fifo Method And Lifo Method.
What is the primary difference between FIFO and LIFO methods?
The primary difference lies in the assumption regarding the flow of inventory. FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, while LIFO assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first.
Which method is more commonly used?
FIFO is more commonly used as it conforms to the general flow of inventory in most businesses. However, LIFO may be advantageous in certain industries, such as those experiencing significant inflation.
How does the choice of method impact financial statements?
The choice of method can impact the reported gross profit, net income, and inventory value. FIFO typically results in higher gross profit and lower inventory value during periods of rising prices, while LIFO has the opposite effect.