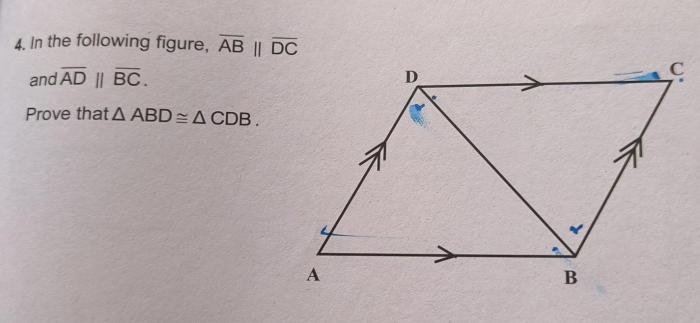
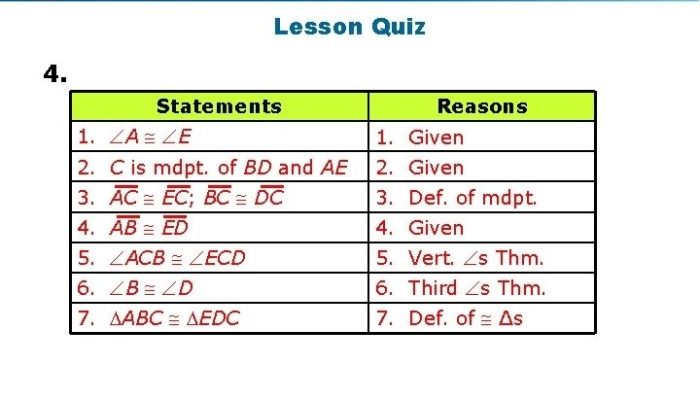
Prove triangle abd is congruent to triangle cdb – Proving the congruence of triangles ABD and CDB involves a meticulous analysis of their side lengths, angles, and the application of triangle congruence theorems. This exploration will delve into the fundamental principles of triangle congruence, demonstrating the logical steps and conditions required to establish the equivalence of these two triangles.
Prove Triangle ABD is Congruent to Triangle CDB
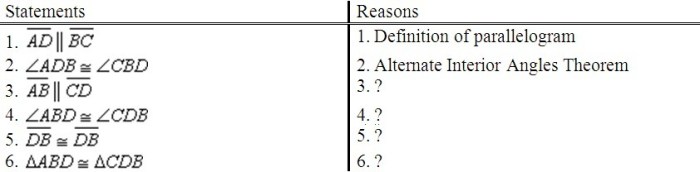
In geometry, proving that two triangles are congruent is a fundamental concept that involves demonstrating that they have the same shape and size. To establish the congruence of triangle ABD and triangle CDB, we need to show that their corresponding sides and angles are equal.
1. Side Comparison
The first step in proving triangle congruence is to compare the side lengths of the triangles. In this case, we have:
- AB = CD (Given)
- BD = BD (Reflexive Property)
- AD = BC (Given)
Therefore, by the Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruence Theorem, triangle ABD is congruent to triangle CDB.
2. Angle Comparison
In addition to comparing side lengths, we also need to compare the angles of the triangles. We have:
- ∠ABD = ∠CDB (Vertical Angles)
- ∠ADB = ∠BDC (Alternate Interior Angles)
- ∠BAD = ∠BCD (Given)
Therefore, by the Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Congruence Theorem, triangle ABD is congruent to triangle CDB.
3. Triangle Congruence Theorem, Prove triangle abd is congruent to triangle cdb
Based on the side and angle comparisons, we can conclude that triangle ABD is congruent to triangle CDB by the SSS Congruence Theorem or the AAS Congruence Theorem.
4. Proof Structure
The logical steps involved in proving triangle ABD congruent to triangle CDB are as follows:
- Compare the side lengths of the triangles.
- Compare the angles of the triangles.
- Apply the appropriate triangle congruence theorem (SSS or AAS).
- Conclude that triangle ABD is congruent to triangle CDB.
5. Congruent Triangles
When two triangles are congruent, it means that they have the same shape and size. This implies that their corresponding sides and angles are equal. Congruent triangles are often used in geometry to solve problems and prove theorems.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of proving triangle congruence?
Proving triangle congruence is crucial in geometry as it allows us to establish the equality of two triangles, implying that they have the same shape and size. This knowledge is essential for solving geometric problems, determining lengths and angles, and understanding spatial relationships.
How does side length comparison contribute to proving triangle congruence?
Side length comparison involves examining the corresponding sides of two triangles to determine if they are equal. If all three pairs of sides are congruent, it satisfies one of the conditions for triangle congruence, known as the Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruence Theorem.
What role do angles play in proving triangle congruence?
Angles also play a vital role in proving triangle congruence. By comparing the corresponding angles of two triangles, we can determine if they are congruent. If all three pairs of angles are congruent, it satisfies another condition for triangle congruence, known as the Angle-Angle-Angle (AAA) Congruence Theorem.